Web3 is a new generation of the internet that helps in interlinking data through a decentralized mechanism to ensure better personalization in user experiences. The foundations of web 3.0 have been developed on the technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, semantic web, and machine learning. Each technology serves a critical role in defining the key traits of web3, such as transformed user experiences, decentralization, and openness.
While blockchain can ensure decentralization as one of the top web 3.0 features, you must also identify how the semantic web defines web3 functionalities. The semantic web basically ensures that machines in the web3 ecosystem cannot only understand data but also interpret the underlying context. Decentralisation remained one of the elusive concepts in the domain of technology for many years. The use of decentralization could put a system at risk of new vulnerabilities alongside increasing the need for resources. However, blockchain and the notion of web 3.0 have proved the possibility of introducing decentralization in an efficient, secure, and resourceful manner.
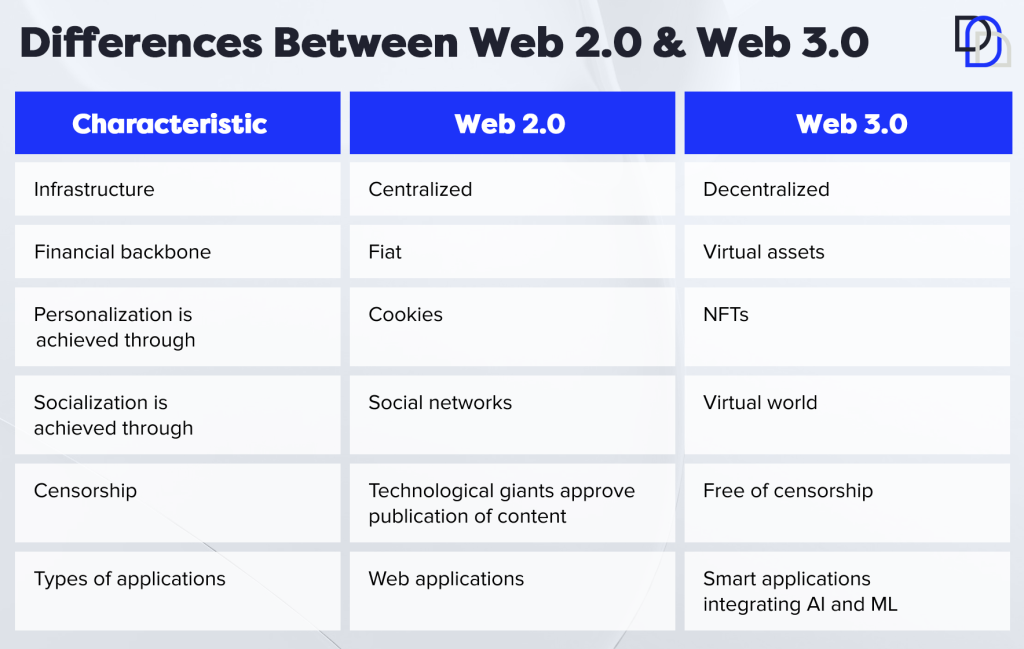
The Importance Of Web 3.0 and Its Differences with Web 2.0
If you take a closer look at the current web all you can do is contribute and share content on different websites or digital platforms with multiple digital identities across different media. On top of it, you don’t have any control over the data you create or the personal information you provide for accessing different services and applications.
Web 3.0 plans on changing the existing narrative by introducing blockchain technology and artificial intelligence into the play. Technological advancements like blockchain and artificial intelligence could help in providing interactive and dynamic user experiences on web 3.0. Most important of all, web3 aims to redefine the online experiences of users with fundamental changes in the structure of the web. At the same time, web3 would also pursue the objective of democratizing almost all aspects pertaining to the internet.
For example, secure storage of data in a distributed network of nodes could help in removing centralized servers. Without any centralized servers, web 3.0 can definitely ensure a lack of censorship or intervention by central authorities, thereby ensuring the democratization of the internet.
Is Web 3.0 Really Necessary?
The attention to web3 characteristics is reasonable considering the necessity for a major shift in dealing with data and web applications. Almost 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated every day in 2023, with 40% of it attributed to machine-generated data. On the other hand, estimates point out that the world would have around 450,000 IoT devices linked to the internet every minute.
The growing volume of data at an unbelievably faster rate than ever before is one of the pressing concerns for web users. Web3 can not only ensure data security but also empower users with control over their own data. Considering the necessity of data security, decentralization, and the creation of unique digital identities in the new generation of the web, it is important to consider how web3 can introduce significant value improvements for users.
Layers In Architecture Of Web 3.0
Let’s take a look at the important layers in the architecture of web3 to identify the significant features. As an evolving concept for the future of the web, web 3.0 would feature many distinctive traits. It is necessary to understand the individual layers in web3 to estimate the significance of key web 3.0 features for the future of the internet. Here are the distinct layers which differentiate web3 from the previous versions.
Edge Computing
Web2 also features edge computing as it modifies the largely commercial personal computer technology for data centers. On the other hand, web 3.0 has been transferring data centers to the edge, thereby bringing back control into the hands of users.
Decentralized Networks
One of the notable entries among web3 characteristics generally refers to decentralized networks. Decentralized data networks are an integral component of the web3 architecture, and they help users in trading or exchanging data without intermediaries, loss of ownership, or jeopardizing user privacy. Web 3.0 considerably emphasizes the notion of “decentralized data,” thereby implying the allocation of data control to consumers.
AI and ML
The other significant technological catalysts for web3 would refer to artificial intelligence and machine learning. Advancements in AI and ML have moved up to a level where they can make proactive, relevant, and useful predictions and decisions. The incorporation of AI and ML powers many of the top web3 features and expands the usability of web3 beyond targeted marketing.
What Web 3 Means For Tech Businesses
The upcoming decade will surely be a period of fundamental technological transformation that will change the way people interact with companies and their solutions. It will be the period of ambient experience strengthening the role of intuitive interfaces and of-the-way affordances to better cater to the needs of users. Thus, companies developing technologically breakthrough solutions should focus on making them easy to understand for users through interactive education and the elimination of any possible barriers. Only companies that take cybersecurity seriously will be relevant and successful. Right now, most cryptocurrencies don’t take cybersecurity seriously. But forces inside and outside Web 3.0 will make cybersecurity a definite must-have.
The Three Pillars Of Web3
According to Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, the Semantic Web can be considered an extension of the existing Web. The Semantic Web is a new form of web content wherein data is organized so as to be decipherable by machines rather than humans. Semantic Web technologies enable people to create data stores on the web, build vocabularies, and write rules for handling data.
Semantic capabilities coupled with NLP enable computers to grasp information at the level of a human being. As a result, they grow smarter and are better able to meet the demands of their customers. NLP assists computers in understanding, interpreting, and manipulating human language so they would be more human-like and comprehend the presented data better, resulting in more precise and prompt solutions and responses.
Personalization: Web 3.0 takes personalization to the next level. Real-time data integration can provide a more meaningful frame for online interactions and interests. Adopting the right business model can help businesses provide a significantly improved customer experience and offer them rich possibilities for advertising and promotion.
Mobile-First Experiences: Providing end users with a mobile-first experience is a must if you want to capitalize on Web 3.0 and better engage with and reach your target audience. Businesses that do not adapt to this trend are in danger of being left behind. Not only do today’s consumers want an integrated omnichannel experience, but they also demand easier and faster access to information.
Ubiquity: Web 3.0 entirely changes the way people access data as they go beyond PCs and smartphones and access content anytime, anywhere through any number of devices. Although Web 2.0 is already ubiquitous, the Internet of Things (IoT) is taking it to a whole new level, and it’s here to stay.
Bottom Line
The distinct features of web 3.0 paint it as a revolutionary paradigm shift in how we use the internet. An outline of the top web 3.0 features reflects the significant improvements web3 brings over its predecessor. The notable features of web 3.0 would include the semantic web, decentralization, artificial intelligence, connectivity and ubiquity, and spatial computing. The prominent features of web 3.0 would distinguish the principles of the new generation of the web. At the same time, the features would also define the appeal of web3 solutions to users.



